Despite what you might think, hair loss in women is very common. In fact, more than 50% of American women will suffer from hair loss at some point in their life. There are two common types of hair loss in women: Androgenetic Alopecia and Telogen Effluvium.
Androgenetic Alopecia:
Androgenetic alopecia (AGA), or hereditary baldness. In women, hair loss manifests itself according to the female pattern (see below). The cause of Androgenetic Alopecia is a genetic, it is hereditary. The hair loss in Androgenetic Alopecia is caused by the male hormone testosterone being converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It can be said that DHT is the biggest enemy of hair: it shrinks the hair follicles. Hair can no longer grow from these hair follicles, or only much thinner hair will grow from them. The female form of hereditary hair loss is chronic hair loss and thinning hair. Typically, the hair in the middle of the head gradually becomes thinner. Because of this, the scalp becomes visible through the hair.
Unlike in men, hair loss is more common at a later age in women, the process is much slower and it rarely leads to bald spots. Women’s hair is very sensitive. The hair responds quickly to physical changes or problems. Hair follicles go into resting phase quicker, causing the hair to fall out and stop growing. In telogen effluvium or telogen hair loss, there is an acute and excessive loss of hair. There is a lot of hair loss, but no real bald spots appear. The hair loss can occur suddenly and can be so severe that it becomes thinner in a really short time, but it can also begin slowly and last longer. The hairs that fall out can be recognized by a small bulb of keratin at the root end of the hair.
Telogen Effluvium:
Telogen Effluvium is generally caused by: Medication (anticoagulants, antihypertensives, starting or stopping the pill), a diet that is inadequate in vitamins and minerals such as vitamin B6 and B12, iron, zinc and amino acids, pregnancy or childbirth. Menopause can trigger Telogen Effluvium, as well as thyroid disorder, stress, rapid weight loss. Cancer treatments usually lead to Anagen Effluvium, an abrupt stop in the growth phase.
There is an important distinction between hereditary hair loss and telogen hair loss. For telogen hair loss, it is in some cases possible to eliminate the cause. This is never possible for hereditary hair loss. And yet, the effects of both types of hair loss are the same: the hair will grow less long and thick and the hair follicles remain longer in their resting phase. Because of this, the treatment for hair loss in women is mostly the same. Fortunately, there are several ways to effectively combat hair loss.
There are a few ways to stimulate new hair growth and improve the condition of the hair and scalp:
- Microneedling by a professional, in combination with Peptide treatments, as well as at home dermaroller applications.
- Shampoos and conditioner with hair growth stimulating ingredients
- Nutritional supplement with the important nutrients for healthy hair growth and hair stimulating extracts.
- Laser therapy
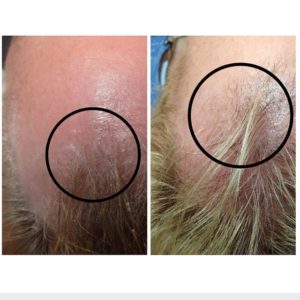 At the beginning of hair loss, when it is not very visible, a good foundation can be laid simply by using a shampoo and nutritional supplement. If you want a better effect or if your hair loss is already clearly visible, it is advisable to start using more advanced treatments.
At the beginning of hair loss, when it is not very visible, a good foundation can be laid simply by using a shampoo and nutritional supplement. If you want a better effect or if your hair loss is already clearly visible, it is advisable to start using more advanced treatments.
As you can see by the photo of this woman treated with a combination of peptides and microneedling, the results are visible. If you would like more information about whether microneedling will work for you, please give us a call for a free, no obligation consultation!